What’s in a mountain’s name?
Sometimes it’s the history of a mountain, like Mount Marathon, named for the annual race run there since 1915. Sometimes it’s just the plain geography, like Flat Top Mountain in Anchorage, which has, well, a flat top.
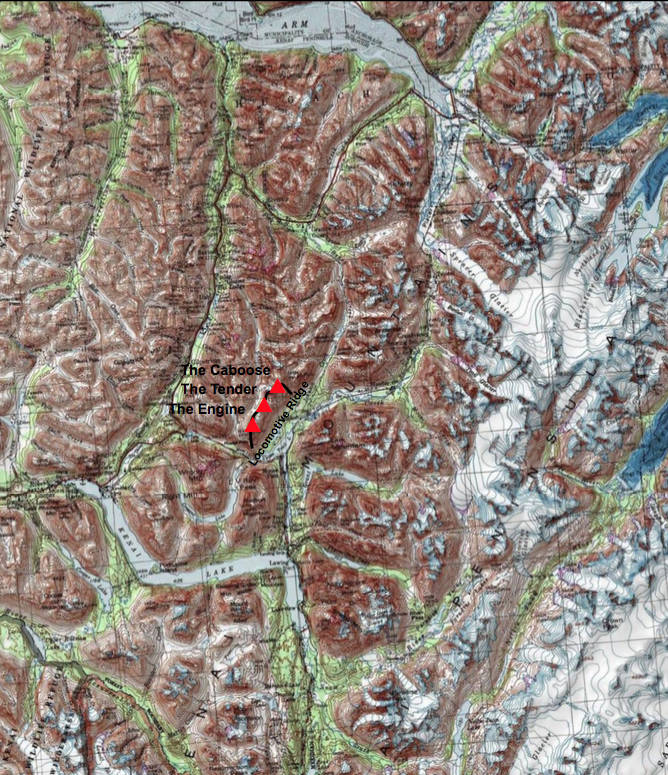
Other times, mountains are named for their significance to an area and the people that live nearby. That was the idea behind the Mountaineering Club of Alaska’s proposal to name a ridge near Moose Pass “Locomotive Ridge,” which was submitted in a request to the Alaska Department of Natural Resources in March.
Two mountaineering brothers who lived in Moose Pass briefly in the late 1960s have asked the Alaska Historical Commission, a division under DNR, to formally name three peaks and a ridge. If the request is granted, the ridge will be named Locomotive Ridge, with peaks named the Engine, the Tender and the Caboose.
Winford Bludworth, one of the proposers, wrote in a January 2015 letter to the Alaska Railroad Corporation’s board of directors that he lived and worked in the Moose Pass area working on the railroad between the spring of 1969 and the spring of 1970, climbing the mountains in the area. When they were climbing, they noticed that the ridge to the north of Lower Trail Lake looked like a train head south, he wrote.
“The Engine, at 4,950 feet elevation, is just fixing to cross Seward Highway,” he wrote. “It is an old steam engine with a cab, smoke stack, and even a rake on the front. To our eyes it looks so close to a real train engine from that point. Right north of the mountain we call the Engine is the Tender, at 4,760 feet elevation. That mountain makes a good tender coming along behind the engine. The next mountain, at 5,050 feet elevation, does not look like a caboose or any other rail car, but we call it the Caboose.”
Bludworth and his brother climbed the peaks in 1969, which were then unclimbed and unnamed, he wrote. The names they gave them never caught on, but the Mountaineering Club of Alaska recognizes Bludworth and his brother as the first ascenders, he wrote.
The Alaska Railroad Corporation has long had a significant presence on the eastern Kenai Peninsula and in Moose Pass, with a depot there that has since been closed. The board of directors supported the naming effort, according to a letter returned to Bludworth in March 2015.
It’s a fairly lengthy process to formally name a geographical feature on federal and state maps. The namer has to submit an application to the Alaska Historical Commission, which reviews it and asks for public input before taking it back to the commission members for approval. The commission then forwards them to the U.S. Board on Geographic Names for final approval. There are a number of stipulations that set guidelines for names as well — for example, a feature can’t be named after a person unless the person has been dead for at least five years.
The Kenai Peninsula Borough Assembly was asked for its opinion about the name, and chose to refuse its support for the application. The main reason was because the Moose Pass Advisory Planning Commission and the borough Planning Commission both refused their support, with the Moose Pass commission saying that locals didn’t recognize or use the name Locomotive Ridge or any of the peak names. The proposers also didn’t live in Moose Pass for long, and one peak close by already has a name — Moose Peak.
The Moose Pass Advisory Planning Commission unanimously voted down the resolution supporting the naming at its June 6 meeting, according to the minutes submitted to the assembly. The Planning Commission also unanimously voted it down. Without much debate, the assembly took the planning commissions’ lead, voting it down 8-1, with only assembly member Paul Fischer voting in favor.
Joan Antonson, the deputy state historic preservation officer, said the assembly’s word doesn’t mean the decision is necessarily final, but the Alaska Historical Commission does listen to public opinions when deciding to name features.
“They do listen to the input, and that’s what they need to know,” she said. “The best reason to name anything is what the people use and what the local people want. That is high on their priority list when considering the name.”
The public can still weigh in on the proposed name until June 30, when the comment period closes. Comments can be submitted to the Alaska Historical Commission by mail at 550 West 7th Avenue, Suite 1310, Anchorage, Alaska, 99501, or by email to dnr.oha@alaska.gov.
Reach Elizabeth Earl at elizabeth.earl@peninsulaclarion.com.