JUNEAU — Environmentalists lost the first round of their legal battle over a major oil project on Alaska’s petroleum-rich North Slope on Monday as a judge rejected their requests to halt immediate construction work related to the Willow project, but they vowed not to give up.
The court’s decision means ConocoPhillips Alaska can forge ahead with cold-weather construction work, including mining gravel and using it for a road toward the Willow project. Environmentalists worry that noise from blasting and road construction could affect caribou.
U.S. District Court Judge Sharon Gleason said she took into account support for the project by Alaska political leaders — including state lawmakers and Alaska’s bipartisan congressional delegation. She said she also gave “considerable weight” to the support for Willow by an Alaska Native village corporation, an Alaska Native regional corporation and the North Slope Borough, while also recognizing that project support among Alaska Natives is not unanimous.
Environmental groups and an Alaska Native organization, Sovereign Iñupiat for a Living Arctic, had asked Gleason to delay construction related to Willow while their lawsuits are pending. They ultimately want Gleason to overturn the project’s approval, saying the U.S. Bureau of Land Management failed to consider an adequate range of alternatives.
Gleason said the construction work that ConocoPhillips Alaska plans for this month is “substantially narrower in scope than the Willow Project as a whole,” and the groups did not succeed in showing it would cause irreparable harm before she makes a decision on the merits of the cases.
Rebecca Boys, a company spokesperson, said ConocoPhillips Alaska appreciates the backing it has received from those “who recognize that Willow will provide meaningful opportunities for Alaska Native communities and the state of Alaska, and domestic energy for America.”
To prevent the worst of climate change’s future harms, including even more extreme weather, the head of the United Nations recently called for an end to new fossil fuel exploration and for rich countries to quit coal, oil and gas by 2040.
A ConocoPhillips Alaska executive, Stephen Bross, warned in court documents that an order blocking construction could make it “impossible” for the project to begin production by Sept. 1, 2029, and the company risks having its leases expire if the unit hasn’t produced oil by then.
One of the suits, filed by Earthjustice on behalf of numerous environmental groups, says the government analyzed an inadequate range of alternatives “based on the mistaken conclusion that it must allow ConocoPhillips to fully develop its leases.” It also says the environmental review underlying Willow’s approval didn’t assess the full climate consequences of authorizing the project because it didn’t analyze greenhouse gas emissions from other projects in the region that could follow.
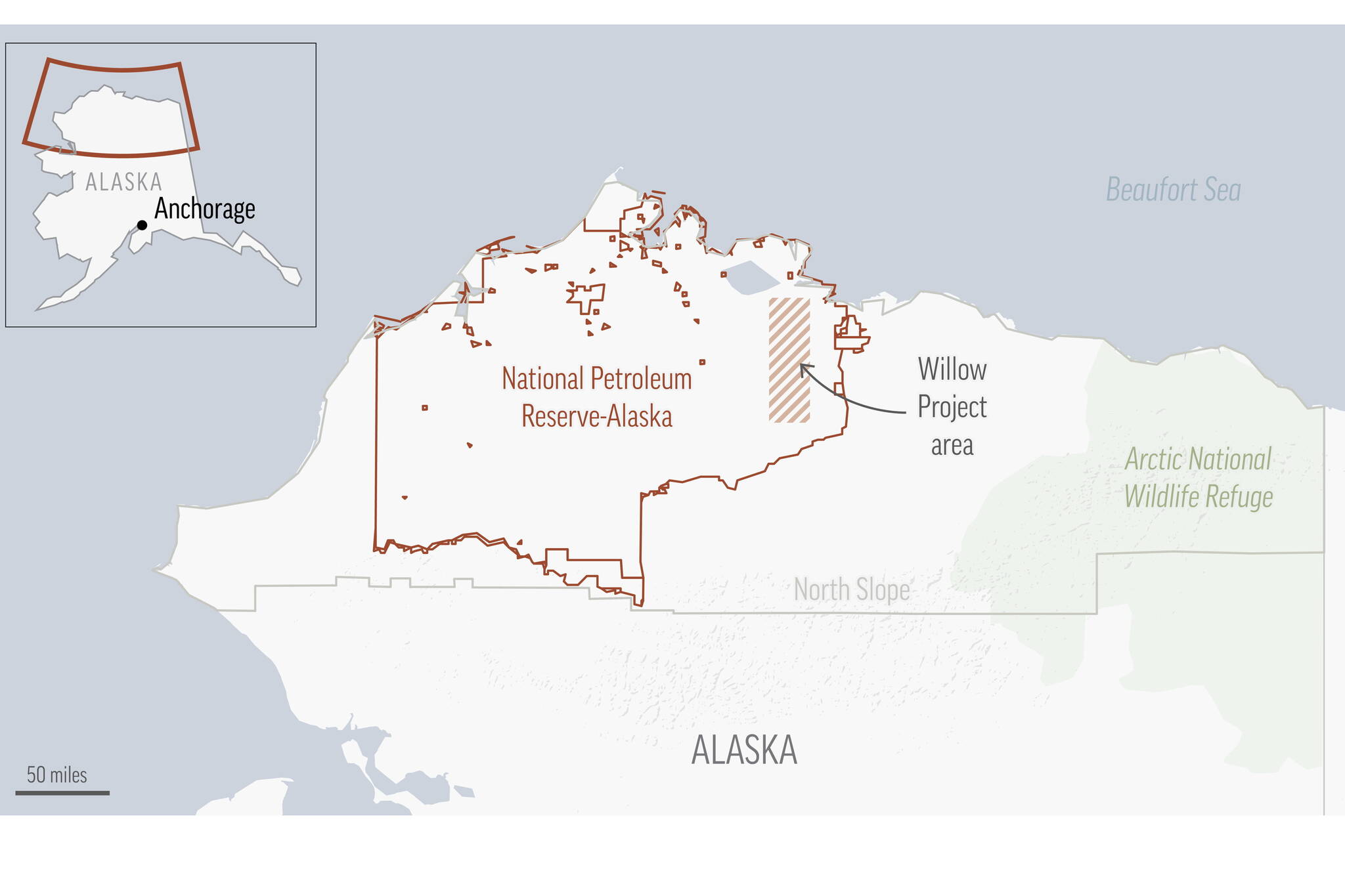
The Willow project is in the northeast portion of the National Petroleum Reserve-Alaska, where there has been debate over how much of the region should be available to oil and gas development.
The Biden administration in 2022 limited oil and gas leasing to just over half the reserve, which is home to polar bears, caribou, millions of migratory birds and other wildlife. There are multiple exploration and development projects within 50 miles of the Willow project, including other discoveries being pursued by ConocoPhillips Alaska, the state’s largest oil producer.
The other lawsuit, filed by Trustees for Alaska on behalf of Sovereign Iñupiat for a Living Arctic and environmental groups, said federal agencies failed to take a “hard look at the direct, indirect and cumulative impacts” of the Willow project and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service failed to address impacts to polar bears, a threatened species under the Endangered Species Act.
Bridget Psarianos, lead staff attorney with Trustees for Alaska, said in a statement that Gleason’s decision is “heartbreaking for all who want to protect local communities and prevent more devastating climate impacts in the Arctic and around the world. We will do everything we can to protect the region while the merits of our case get heard.”
Erik Grafe, deputy managing attorney for Earthjustice in Alaska, said while this round of legal challenges “did not produce the outcome we had hoped for, our court battle continues.”
Justice Department lawyers had argued that last month’s decision by the Biden administration approving Willow was “based in science and consistent with all legal requirements.” They also said the environmental review thoroughly analyzed emissions related to the use of oil produced by the project and called the analysis sought by Earthjustice overreaching.
State political leaders, including Republican Gov. Mike Dunleavy, and labor unions have touted Willow as a job creator, expected to produce up to 180,000 barrels of oil a day. That’s significant, because major existing fields are aging and the flow of oil through the trans-Alaska pipeline is a fraction of what it was at its peak in the late 1980s.
Many Alaska Native leaders on the North Slope and groups with ties to the region have argued that the project is economically vital for their communities. Nagruk Harcharek, president of the Voice of Arctic Iñupiat, whose members include leaders from across much of the North Slope, called Gleason’s decision “another step forward for Alaska, Alaska Native self-determination, and for America’s energy security.”
But some Alaska Native leaders in the community closest to the project, Nuiqsut, have expressed concerns about impacts to their subsistence lifestyles and worried that their voices haven’t been heard.
Using the oil that Willow would produce over the 30-year life of the project would emit roughly as much greenhouse gas as the combined emissions from 1.7 million passenger cars over the same period. Climate activists say the project flies in the face of President Joe Biden’s pledges to cut carbon emissions and move to clean energy.
The administration has defended the decision on Willow and the president’s climate record. Interior Secretary Deb Haaland, who opposed Willow when she was a New Mexico congresswoman, last month called the project a “difficult and complex issue” involving leases issued by prior administrations. She said there was “limited decision space” and the administration had “focused on how to reduce the project’s footprint and minimize its impacts to people and to wildlife.”
Global demand for crude is expected to continue rising, according to industry analysts and the U.S. Energy Information Administration.