Alaska could have federal help in cleaning up so-called “forever chemicals” that have contaminated water and soil in the state. But first, a bill would need approval from the U.S. Senate and President Donald Trump.
A bill was passed by the U.S. House of Representatives Friday that would require the Environmental Protection Agency to designate per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, commonly called PFAS, as hazardous substances under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act of 1980. That’s the act that provides federal Superfund, which gives the EPA funds and authority to clean up uncontrolled or abandoned hazardous-waste sites.
That means PFAS-contaminated sites could be eligible to become Superfund sites if the bill becomes law.
PFAS are a group of long-lasting, man-made chemicals that have been linked to low birth weights, cancer, thyroid hormone disruption and negatively affecting the immune system, according to the EPA. Health concerns regarding water supply contamination led in November to residents of Gustavus having their blood tested.
There are currently 10 Superfund sites in Alaska, according to EPA. A Superfund site assessment process that considers the threat hazardous substances pose to people and the environment helps determine whether an area becomes a Superfund site.
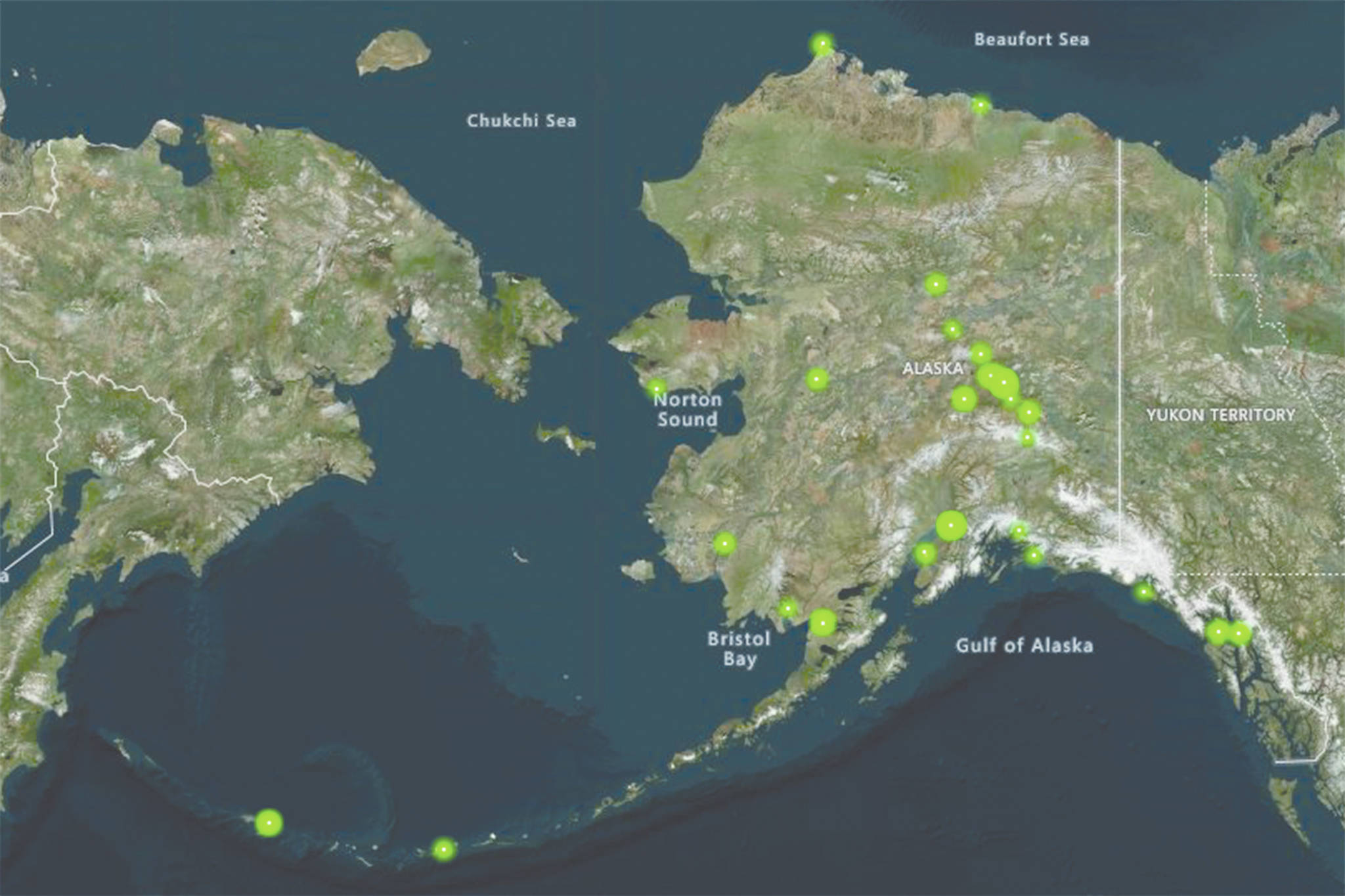
PFAS contamination in Alaska is primarily related to the use of aqueous film-forming foams, according to the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation, and that’s reflected in a list of PFAS-contaminated sites.
DEC’s list of PFAS sites is long and names cities and military bases throughout the state. Sites listed include Juneau, Amchitka, Eielson Air Force Base, Soldotna, King Salmon, North Pole, Galena, Elmendorf Air Force Base, Fairbanks, Fort Greely, Adak, Fort Richardson, Coldfoot, Salcha, Prudhoe Bay, Fort Wainwright, Paxson, Stevens Village, Anchorage, Clear, Yakutat, Minto, Kenai, Utqiagvik, Nome, Bethel and Valdez.
Soil and water samples taken near Juneau International Airport and Hagevig airport showed PFAS present. The contamination was not near known sources of drinking water, according to City and Borough of Juneau.
While many communities in Alaska have some level of PFAS contamination, it is not an Alaska-specific problem. An interactive map of PFAS contamination created by the Environmental Working Group, a nonprofit activist group that researches toxic chemicals and water pollutants among other things, shows tight clusters of contamination in the northeastern U.S., Michigan, Kentucky and Southern California.
The prevalence of PFAS seems to be reflected in broad support for the PFAS Action Act, which passed with bipartisan support. Two hundred twenty-three Democratic representatives and 24 Republican representatives, including Alaska’s Rep. Don Young, voted for it.
“Too many Alaskan communities, particularly those in close proximity to military bases, have faced challenges in remediating PFAS contamination,” Young said in a release. “It has been one of my priorities this Congress to address the issue of PFAS contamination in our state and across the country.”
Superfund typically forces those responsible for contamination to either perform cleanups or reimburse the government for EPA-led cleanup work, according to EPA.
However, that could be financially devastating for small airports that were required to use contaminating foam by the Federal Aviation Administration.
Zack Brown, press secretary for Young, told the Empire via email the bill includes provisions to exempt parties, such as municipal airports, that were required to use PFAS-containing foam.
“The EPA Superfund program includes a process to thoroughly examine and identify responsible parties on a case by case basis,” Brown said.
When there isn’t a viable responsible party, Superfund provides funds for the cleanup process.
While the bill did not pass via a party-line vote, it was favored more by Democrats than Republicans, which could indicate it’s less likely to pass in the Republican-majority Senate. However, it would seem likely to have support from Alaska’s Republican senators.
Spokespeople for Sens. Dan Sullivan and Lisa Murkowski did not return calls or emails seeking comment Friday, but Murkowski was among a group of bipartisan senators who introduced the Senate’s PFAS Action Act. Sullivan was part of a bipartisan group of lawmakers who introduced a bill to protect firefighters from PFAS.
If both the House and Senate do pass the bill, it would likely be vetoed by President Donald J. Trump.
On Jan. 7, the White House issued a statement criticizing the PFAS Action Act.
The White House stated the bill “would create considerable litigation risk, set problematic and unreasonable rulemaking timelines and precedents, and impose substantial, unwarranted costs on Federal, State, and local agencies and other key stakeholders in both the public and private sectors.”
It concluded by stating if the bill makes it to the president, his advisers would recommend that he veto the bill.
Contact reporter Ben Hohenstatt at (907)523-2243 or bhohenstatt@juneauempire.com. Follow him on Twitter at @BenHohenstatt.